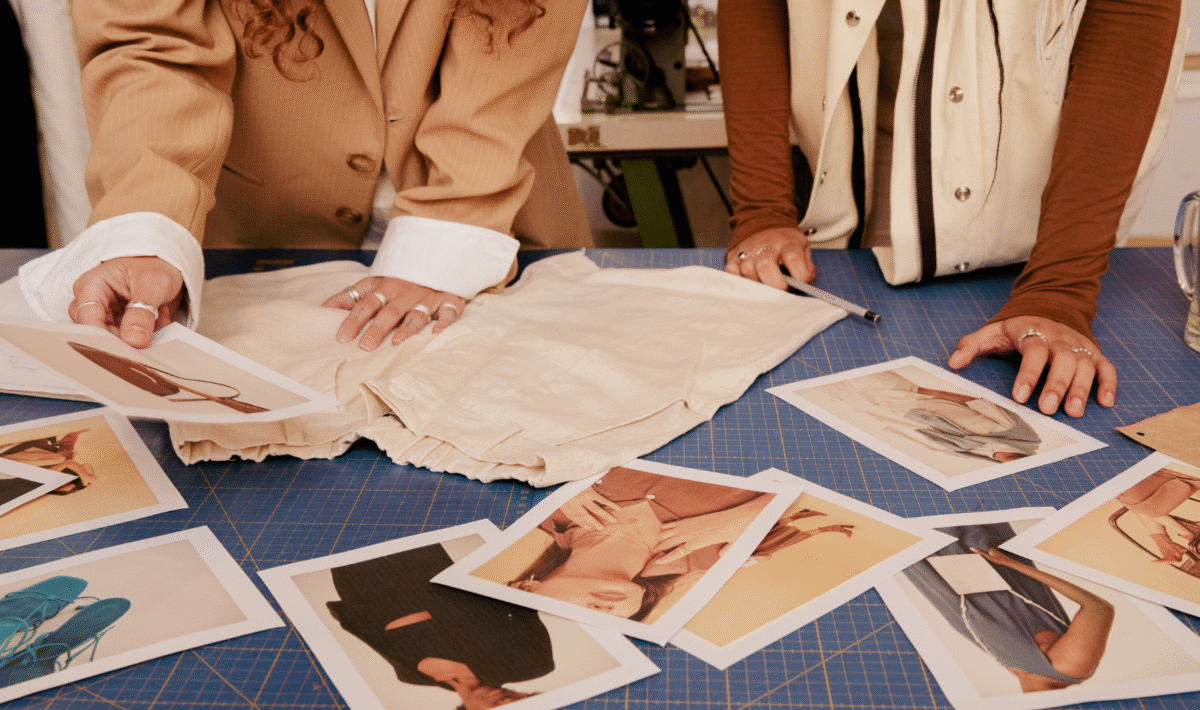
The fashion industry significantly impacts the environment, often leading to negative consequences such as pollution and waste. Making sustainable fashion choices is essential for individuals who wish to contribute to a healthier planet. By opting for sustainable options, consumers can reduce their ecological footprint and support ethical practices.
Sustainable fashion prioritizes quality over quantity, focusing on durable materials that last longer. This not only benefits the environment but also encourages a more mindful approach to shopping, where individuals value their clothing choices. As awareness grows, more brands are embracing sustainable practices, making it easier for consumers to make responsible decisions.
Engaging with sustainable fashion empowers individuals to advocate for a more equitable industry. It fosters a culture of transparency and accountability, encouraging companies to adopt fair labor practices and reduce their environmental impact. Making sustainable fashion choices ultimately contributes to a more ethical and sustainable future for all.
Understanding Sustainable Fashion
Sustainable fashion emphasizes eco-friendly practices and ethical production. Important concepts include defining sustainable fashion, contrasting it with fast fashion, and exploring circular fashion within the circular economy.
Defining Sustainable Fashion
Sustainable fashion seeks to minimize environmental impact and promote ethical practices throughout the fashion supply chain. This includes using organic materials, reducing waste, and ensuring fair labor practices.
Key aspects of sustainable fashion encompass:
- Ethical production: Fair wages and safe working conditions for workers.
- Eco-friendly materials: Usage of organic cotton, recycled fabrics, and biodegradable materials.
- Transparency: Brands must disclose their production processes and supply chains.
By prioritizing these factors, sustainable fashion encourages consumers to make choices that support environmental health.
Sustainable Fashion vs. Fast Fashion
Sustainable fashion and fast fashion represent two opposing philosophies. Fast fashion is characterized by rapid production cycles and low-cost items that prioritize trends and volume over quality.
Key differences include:
- Production methods: Fast fashion often employs harmful practices, like pollution and exploitation.
- Longevity: Sustainable pieces are designed for durability, contrasting with fast fashion’s disposable nature.
- Environmental Impact: Fast fashion significantly contributes to landfill waste and carbon emissions.
Choosing sustainable fashion enables consumers to support eco-conscious brands and reduce their overall environmental footprint.
Circular Fashion and Circular Economy
Circular fashion functions within the broader framework of a circular economy, which focuses on sustainability through resource regeneration. In this model, garments are designed for longevity, repairability, and recyclability.
Core principles of circular fashion include:
- Recycling and Upcycling: Transforming old materials into new products.
- Rental and Resale: Facilitating ownership models that extend garment lifespans.
- Waste Minimization: Designing for a lifecycle that reduces waste generation.
A circular economy promotes resource efficiency and encourages responsible consumption, aligning with sustainable fashion goals.
Environmental Benefits of Sustainable Fashion Choices
Sustainable fashion choices significantly reduce environmental impact, promoting a healthier planet. Key factors include waste reduction, lower carbon emissions, and the use of sustainable materials that contribute to less resource depletion.
Reducing Environmental Impact
Sustainable fashion significantly minimizes environmental impact by addressing various harmful practices in the textile industry. Traditional fashion relies heavily on fossil fuels for production, which contributes to resource depletion and climate change. In contrast, sustainable practices encourage the use of eco-friendly materials and production methods that are less taxing on the environment.
By choosing brands focused on sustainability, consumers can support practices that utilize organic materials, such as organic cotton and biodegradable fabrics. This shift not only conserves resources but also reduces pollution associated with conventional textile production.
Waste Reduction and Recycling
Textile waste is a major contributor to landfills, with approximately 92 million tons produced globally each year. Sustainable fashion emphasizes waste reduction through practices like upcycling and recycling.
Many brands now engage in circular fashion initiatives, where garments are designed to be reused or recycled at the end of their lifecycle. This minimizes waste and encourages a culture of sustainability among consumers.
Additionally, donating or recycling clothing can extend the life of textiles, keeping them out of landfills. These practices not only decrease textile waste but also promote a more sustainable consumption model.
Lowering Carbon Emissions and Carbon Footprint
The fast fashion industry is responsible for significant carbon emissions, accounting for around 10% of global emissions. Sustainable fashion aims to lower these emissions through several strategies.
Utilizing natural fibers and sustainable materials leads to a smaller carbon footprint compared to synthetic alternatives. For instance, organic cotton production typically requires less energy and water, reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions.
Moreover, brands that prioritize transparency often disclose their carbon footprint, allowing consumers to make informed choices and support lower-impact options. Thus, sustainable fashion plays an important role in combating climate change.
Choosing Sustainable Materials and Natural Fibers
The selection of materials in fashion significantly influences its environmental impact. Sustainable fashion advocates for the use of eco-friendly materials, including organic cotton, recycled fabrics, and natural fibers such as hemp and linen.
Natural fibers are biodegradable, meaning they break down more easily than synthetic materials, which can take hundreds of years to decompose. This not only reduces waste but also alleviates the burden of microplastics in the ecosystem.
Incorporating organic materials promotes agricultural practices that prioritize environmental health and support biodiversity. As consumers lean towards these sustainable materials, the fashion industry can shift towards more responsible sourcing practices overall. Choosing pieces made from these fabrics in everyday categories, like loungewear and sleepwear, including mens pajamas canada (or similar options elsewhere), makes sustainability feel practical and accessible. It’s a simple way to bring conscious choices into daily life while still enjoying comfort and style.
Social and Ethical Impacts of Your Clothing Choices
The choice of clothing has significant social and ethical implications. By opting for sustainable fashion, individuals can contribute to fair working conditions, respect for human rights, and support for local economies. These choices also extend to animal welfare and the promotion of cruelty-free options.
Supporting Fair Wages and Safe Working Conditions
Sustainable fashion often emphasizes fair wages and safe working conditions for garment workers. Many brands committed to ethical practices to ensure that their workers receive a living wage, enabling them to support themselves and their families.
This commitment helps prevent the exploitation of workers, particularly in developing countries where labor laws may be weak. It also reduces the prevalence of child labor, as fair wages enable parents to support their children rather than sending them to work. Consumers can play a significant role in advocating for brands that prioritize these essential standards.
Protecting Human Rights and Ethical Labor Practices
Ethical fashion brands prioritize human rights and labor practices in their supply chains. They strive to ensure that workers are treated with dignity and respect, adhering to international labor standards. This focus helps protect individuals from harassment, discrimination, and unsafe working environments.
By choosing brands that align with these principles, consumers can advocate for change in the industry. Supporting ethical labor practices is crucial for creating a marketplace where human rights are upheld and workers are empowered.
Empowering Local Communities and Traditional Craftsmanship
Sustainable fashion fosters the empowerment of local communities through the support of traditional craftsmanship. Many ethical brands collaborate with artisans who use age-old techniques to create unique garments. This not only preserves cultural heritage but also provides a fair income to these communities.
Investing in local craftsmanship strengthens economies and supports community development. It creates employment opportunities and enables artisans to showcase their skills globally, preserving traditional methods for future generations. Consumers have the power to promote these practices by choosing brands that value local artisanship.
Animal Welfare and Vegan Fashion
The ethical implications of clothing choices extend to animal welfare. Vegan fashion focuses on cruelty-free alternatives that avoid animal-derived materials such as leather, wool, and silk. Brands promoting vegan fashion often prioritize sustainable materials that do not harm animals.
Adopting vegan fashion helps reduce the demand for industries that exploit animals for clothing. Consumers can support cruelty-free brands that align with their values, encouraging the broader fashion industry to adopt more humane practices. The movement towards animal welfare reinforces the importance of ethical considerations in personal fashion choices.
How to Make Sustainable Fashion Choices
Making sustainable fashion choices involves understanding the impact of clothing production and consumption on the environment. Addressing overconsumption and identifying quality pieces can lead to a more sustainable wardrobe. Additionally, awareness of marketing tactics such as greenwashing can empower individuals to make informed decisions.
Building a Sustainable Wardrobe
A sustainable wardrobe starts with choosing clothing made from eco-friendly materials. Natural fibers like organic cotton, linen, and Tencel have a lower environmental impact compared to conventional fabrics. Brands focusing on sustainable practices often highlight their sourcing and production methods.
Diversifying clothing by incorporating second-hand or vintage items can also enhance sustainability. Thrift stores and online platforms offer unique pieces that reduce reliance on fast fashion. Prioritizing brands committed to ethical labor practices promotes transparency in clothing production.
Prioritizing Quality Over Quantity
Focusing on quality over quantity is crucial for sustainable fashion. When individuals invest in well-made garments, they reduce the need for frequent replacements. This shift away from fast fashion minimizes overproduction and waste.
Choosing timeless styles helps avoid the pitfalls of fleeting fashion trends. Classic pieces can be styled in various ways, extending their lifespan. Investing in clothing that is durable, easy to care for, and versatile contributes to a sustainable wardrobe.
Conscious Consumption and Overcoming Overconsumption
Conscious consumption involves thoughtful decision-making about purchases. Creating a personal shopping list can help avoid impulse buys, which often contribute to overconsumption. Reflecting on needs versus wants helps prioritize sustainable choices.
Participating in clothing swaps or rental services can be effective alternatives to purchasing new items. Such practices contribute to a circular economy, minimizing waste from the throwaway culture. Setting limits on new purchases encourages individuals to make mindful decisions.
Navigating Greenwashing
Greenwashing occurs when brands exaggerate their environmental claims to attract consumers. It is essential for individuals to verify sustainability claims by researching brands thoroughly. Look for certifications like GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) or Fair Trade, which indicate genuine commitment to sustainable practices.
Scrutinizing marketing messages can help uncover misleading tactics. Understanding the processes involved in clothing production, such as dyeing and finishing, reveals potential use of harmful chemicals. By being informed, individuals can make choices that align with authentic sustainable development goals.